
Ruby Mines and Rubies are primarily composed of the mineral corundum or aluminum oxide. They are formed under extreme heat and pressure under the earth’s surface. The mineral corundum is made of dense oxygen and aluminum atoms packed inside it. Typically, the mineral is colorless, however, if the aluminum atoms are replaced by other substances, they can become other colors. This process is how the rubies get their deep red hue, more specifically, because of the presence of chromium in their mineral composition.
ORIGIN & FORMATION OF RUBIES
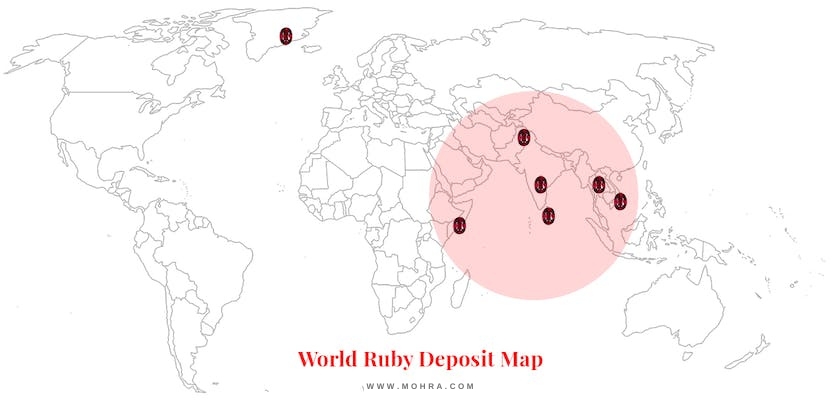
Rubies are mainly found in 3 Origins that have the most production.
- Burmese Ruby
- Thai Ruby
- Mozambique Ruby
- Greenland Ruby
- Sri Lanka Ruby
- India Ruby
- Kashmir Ruby
- Vietnam Ruby
Rare shades of orange and pink ruby are created due to chromium and ferric iron being present. if only 1% of the aluminum atoms are replaced with chromium, the ruby gains its famous deep red color.
However, silica or iron prevent rubies from forming. Both of those minerals are very common in the earth’s crust, thus making rubies rare to find and mine. Furthermore, corundum is also a rare mineral to find.
Besides de deposits found in Mozambique, most ruby mines are found in Asia, in countries such as Myanmar (previously Burma and home to Burmese Rubies), Thailand, India, Pakistan, and Nepal. Rubies were formed as the Asian and Indian subcontinent collided, creating the immense pressure and temperature required, alongside the presence of certain minerals, to form ruby deposits. The formation of rubies date from 50 million years ago.
Further ruby deposits can be found in Madagascar, Montana, and Macedonia.
Most rubies have naturally formed imperfections, developed during the formation process of the stone. They are commonly called ‘rutile needles’ or ‘silk’. These needles are the distinguishing factor between natural stones and lab-created ones.
BURMESE RUBY
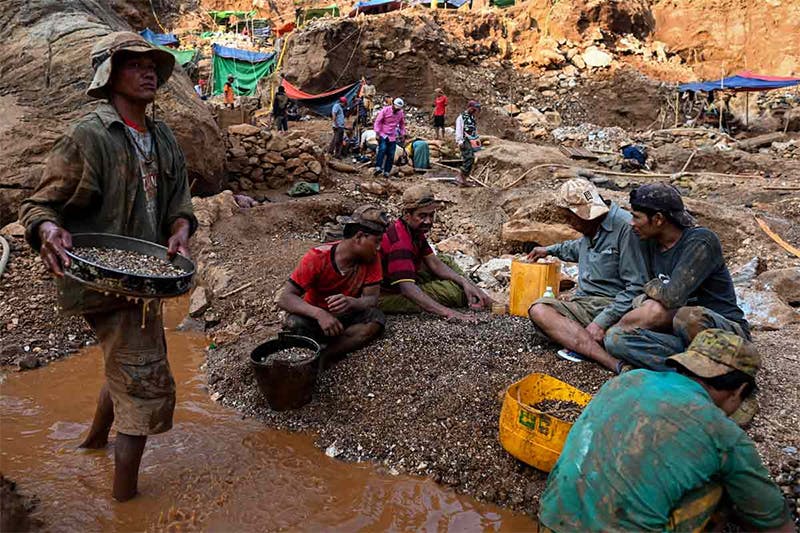

The Burmese Ruby is one of the most precious gemstones known today, and the ruby mines in Burma have produced some of the finest of its kind. It is valued for its rarity, durability, and color, most desired for its dark red color with a slight blue tint. Rubies are found in various mines around the world, however, Pidgeon Blood Rubies from Myanmar, previously Burma, are still some of the most sought out stones, characterized by their rich red color.
Second only to diamonds, the Burmese Ruby is extremely hard, making it the ideal gemstone for a variety of jewelry. However, certain varieties of stone are far more valuable than others, depending on size, region, carat, etc.
THAI RUBY

Thailand is renowned for its colorful gemstones, and the country has prominent ruby mines too. The Asian country has become the center for color gemstone cutting and trade, especially rubies.
It is no surprise that Thai Rubies are synonymous with high-quality, and their gems are often used in jewelry around the globe. Bangkok, the capital, is a well-known center of ruby trade, and also benefits from being a major hub for the import and export of gemstones within southeast Asia, and the rest of the world. Thailand is now a recognized source for high-quality rubies and Blue Sapphire, praised by experts of the industry.
MOZAMBIQUE RUBY

Situated along the Indian Ocean on South eastern coast of Africa, Mozambique’s ruby mines are becoming a source for world-class rubies.
Mozambique shares its borders with other ruby-producing countries, Tanzania and Malawi. The country was a Portuguese colony for almost 500 years and finally gained independence in 1975. Since then, it has been torn by a civil war and flooding in the following decades, which have completely devastated the population.
In recent times, the African country has seen continuous economic growth in agriculture alongside tapping into its rich resources of natural gas, titanium and hydroelectric power. The ruby mines also help stimulate growth but are a more recent element of their economic sector, although it does appear promising for the worldwide supply of rubies.
The region is rich in Corundum, which is the chemical element that constitutes rubies. The compound was originally discovered in the 1500’s, but there was no commercial exploitation until after the country’s independence and civil war. Mozambique ruby began to enter the market around the 1990’s, but they didn’t gain traction until the mid to late 2000’s.
Towards the later half of the 2000’s more substantial ruby mines were discovered in the Niassa and Montepuez regions. By 2010, GIA reports showed that rubies from the country had began to dominate the Thai market, however, many of the mines and sources were unlicensed and untraceable.
In the 2011, a year later, the British company Gemfields partnered with one of Mozabique’s largest ruby mining company to form the Montepuez Ruby Mining Company. This partnership brought improved infrastructure, machinery, and security, thus streamlining the whole process. Since this partnership, the mining in the area has been ramped up and members of the industry are beginning to recognize Mozambique as one of the largest ruby suppliers in the world. We are also one of the leading Gemfields Authorized Auction Partner.
Considering the geography and geology of Mozambique, it would be no surprise that there may be a treasure chest of rubies at the heart of the country. The North Eastern region of the country is at the juncture between the Mozambique Belt and the Zambezi Belt, formed by the famous river. This geological meeting point produces perfect thermal and deformational events, providing perfect temperatures and pressures for rubies, garnets and other minerals to be formed.
Today a small but significant part of the material drawn from the ruby mines has a color and clarity that require no heat treatment. The country is also producing such a high volume of stones that the market is witnessing an influx of a wide range of sizes and qualities that far exceed previous years.
With the country’s continued interest and large quantity of rubies being produced, some large mining corporations have come into conflict with the smaller miners and mining staff being brought in from the dried-up Thai fields. If the African Ruby mines continue to produce stones in record numbers, the potential for more clashes raises. Currently, there appears to be more than enough supply for all mining companies.
